The Heat
Exchanger Theory article provides you with an introduction to the
fundamentals of a heat exchanger and will be useful to understand the concept
of heat exchanger inspection.
To describe this
Theory, you may know we need to heat or to cool process fluids in industrial
plants to facilitate process reactions. So we need to use heat exchangers
either to reduce the temperature or increase the temperature.
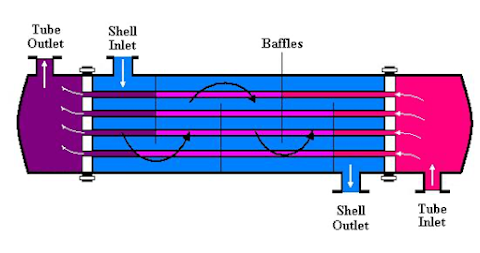
In most heat
exchangers, two fluids are exchanging their heat without direct physical
contact to avoid mixing. This is called indirect heat transfer.
Cooling water
temperature in a hot area is normally above 25 degrees centigrade, and it
depends on the atmospheric and climate conditions. To reach the range of 1 to 5
degrees centigrade, we need to use chilled water, which is already cooled by a
refrigerant.
To reach the
sub-zero temperature, we need to use refrigerant fluid alone, such as R-11 or
propylene. For heating purposes, the mechanism is similar to cooling. We can
use hot intermediate fluid such as hot water or steam and even other hot
process streams.
To proceed on the
heat exchanger theory, we need to know that the meaning of the following
terminologies:
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat is the amount of heat that a
material can exchange without changing its phase. For example, water at 25
degrees centigrade enters the heat exchanger and absorbs the process fluid heat
and exits from the heat exchanger at 35 degrees centigrade.
What is latent Heat?
The latent heat is the amount of heat
transfer that a material exchanges during the change from the liquid phase to
the vapor phase.
Referring to the above definition we are
using saturated steam in heat exchangers, the saturated steam is converted to
liquid and the released heat will heat our process fluid.
Indirect heat transfers are done in
different heat exchangers such as coolers, heaters, reboilers and condensers.
We are calling it
indirect because the two fluids during the heat transfer process are not mixing
together; the heat transfer is done through a metallic surface.
In the above, the
heat exchanger that we are using to eliminate latent heat is called a condenser
and the one that is used to supply steam and heat to the distillation tower is
called a reboiler. We will discuss them in detail in the coming paragraphs.
In all of them, we
are using an intermediate fluid for heat transfer. For the condenser, it is
cooling water, and in the reboiler, it is steam.
To Know More Read Full Article Here: https://sa179tubes.com/the-theory-behind-heat-exchanger/


.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment